| CAS |
300-08-3 |
| Chinese Name |
氢溴酸槟榔碱 |
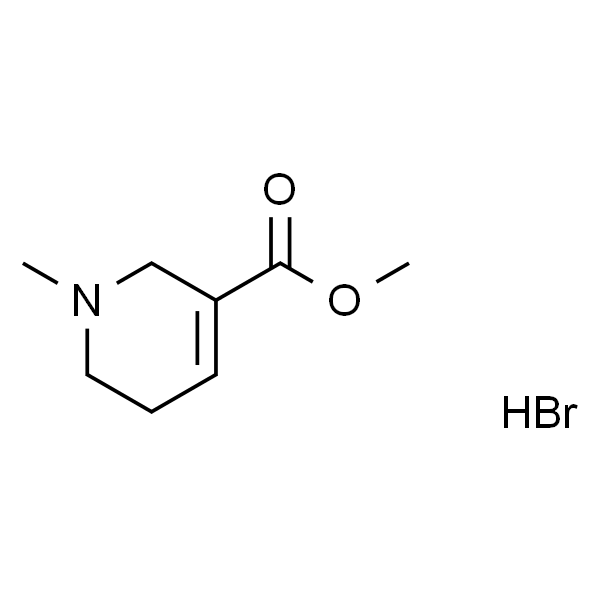
| English Name |
Arecoline Hydrobromide |
| Synonyms |
Arecoline HBr;Arecoline bromide |
| Molecular Formula |
C8H13NO2·HBr |
| Molecular Weight |
236.11 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in Water/DMSO ≥10mg/mL;Soluble in Ethanol ≥5mg/mL |
| Purity |
HPLC≥98% |
| Appearance |
White to off-white Solid |
| Storage |
Powder:2-8℃,2 years;Insolvent(Mother Liquid):-20℃,6 months;-80℃,1 year |
| EC |
EINECS 206-087-3 |
| MDL |
MFCD00039041 |
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=CCCN(C)C1)OC.Br |
| InChIKey |
AXOJRQLKMVSHHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C8H13NO2.BrH/c1-9-5-3-4-7(6-9)8(10)11-2;/h4H,3,5-6H2,1-2H3;1H |
| PubChem CID |
9301 |
| Target Point |
mAChR;nAChR |
| Passage |
Neuronal Signaling;Membrane Transporter&Ion Channel |
| Background |
Arecoline Hydrobromide is an alkaloid that is a partial agonist of the nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Arecoline Hydrobromide can induce oxidative stress and has anti-anxiety and anti-parasitic activities. |
| Biological Activity |
Arecoline, an arecanut alkaloid present in the saliva of betel quid chewers, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of inflammatory oral diseases, including oral submucous fibrosis and periodontitis.[1] A partial agonist of nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, arecoline evokes multiple effects on the central nervous system (CNS), including stimulation, alertness, elation, and anxiolysis. [2] |
| In Vitro |
Arecoline induced the generation of reactive oxygen species and cell cycle arrest at the G1/G0 phase in HaCaT cells without affecting the expression of p21/Cip1. Arecoline-induced epithelial cell death at higher concentrations was caused by oxidative trauma without eliciting apoptosis. Sublethal concentrations of arecoline upregulated the expression of the following stress-responsive genes: heme oxygenase-1; ferritin light chain; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; and glutathione reductase. Additionally,there was a dose-dependent induction of interleukin-1alfa mRNA by arecoline via oxidative stress and p38 MAPK activation.[1] |
| Cell Experiment |
Human keratinocyte cells(of the HaCaT cell line)were treated with arecoline,following which cell viability was assessed using the Trypan Blue dye-exclusion assay,cell growth and proliferation were analyzed using the MTT(3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide)and 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine incorporation assays,cell cycle arrest and generation of reactive oxygen species were examined using flow cytometry,and gene expression changes were investigated using the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction technique.[1] |
| Data Literature Source |
[1]. Thangjam GS,et,al. Regulation of oxidative-stress responsive genes by arecoline in human keratinocytes. J Periodontal Res. 2009 Oct;44(5):673-82.
[2]. Volgin AD,et,al. DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Arecoline. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 May 15;10(5):2176-2185. |
| Unit |
Bottle |
| Specification |
50mg 10mM*1mL in DMSO 100mg |

 English
English
 中文
中文

 Manual Download
Manual Download

