| CAS |
18956-16-6 |
| Chinese Name |
豆蔻明 |
| English Name |
Cardamomin |
| Synonyms |
Alpinetinchalcone |
| Molecular Formula |
C16H14O4 |
| Molecular Weight |
270.28 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO |
| Purity |
HPLC≥98% |
| Appearance |
Light yellow to yellow Solid |
| Storage |
Powder:2-8℃,2 years;Insolvent(Mother Liquid):-20℃,6 months;-80℃,1 year |
| MDL |
MFCD00238554 |
| SMILES |
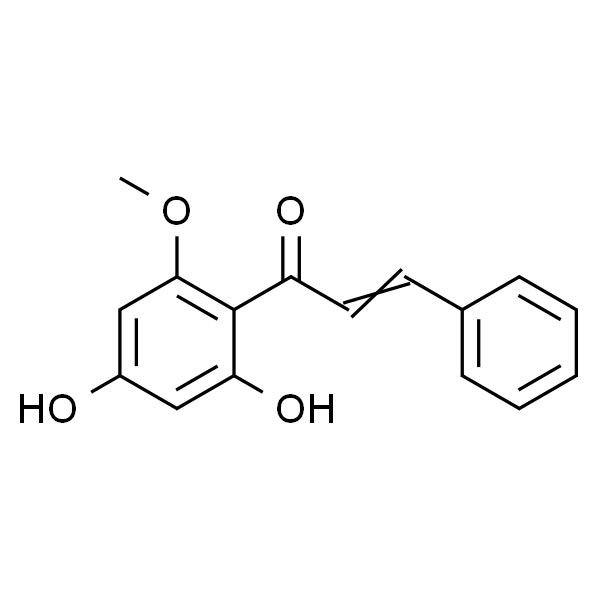
COC1=CC(O)=CC(O)=C1C(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| InChIKey |
NYSZJNUIVUBQMM-BQYQJAHWSA-N |
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H14O4/c1-20-15-10-12(17)9-14(19)16(15)13(18)8-7-11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-10,17,19H,1H3/b8-7+ |
| PubChem CID |
641785 |
| Target Point |
Calcium Channel |
| Passage |
Membrane Transporter&Ion Channel;Neuronal Signaling |
| Background |
Cardamomin is a novel hTRPA1 ion channel antagonist. |
| Biological Activity |
Cardamonin (Alpinetin chalcone)天然存在于良姜属物种的果实中,具有抗炎和抗肿瘤活性。它是一种新型的hTRPA1离子通道拮抗剂,IC50为454 nM,而不与TRPV1和TRPV4相互作用。[1-3] |
| In Vitro |
Cardamonin selectively blocks TRPA1 activation while does not interact with TRPV1 nor TRPV4 channel. A concentration-dependent inhibitory effect is observed with IC50 of 454 nM. Cardamonin does not significantly reduce HEK293 cell viability,nor does it impair cardiomyocyte constriction[1]. In vitro,cardamonin(25 and 50 μM)concentration dependently inhibits endothelium permeability and down-regulates phosphorylation of P38 in rat lung microvascular endothelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharide(LPS). In RAW 264.7 macrophage cells,cardamonin also shows selective inhibition of P38 phosphorylation induced by LPS[2]. Cardamonin inhibits the growth of several cancer cell types including breast cancer,glioblastoma,ovarian,prostate,and lung. Treatment of cardamonin in CRC cell lines induces cell cycle arrest mostly in the S phase of cell cycle. It activates both apoptosis and induces cell cycle arrest to inhibit the cell proliferation. Cardamonin is known to inhibit various signaling pathways which play a major role in the process of inflammation and cancer. This natural product inhibits the phosphorylation and translocation of both STAT3 and NF-κB. Cardamonin also inhibits angiogenesis through downregulation of miR-21 expression[3]. |
| In Vivo |
Cardamonin(30 and 100 mg/kg)significantly elevates the survival rate of septic mice,alleviates ALI and lung microvascular leak,and lowers the serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α,IL-1β,and IL-6[2]. Cardamonin inhibits Azoxymethane-induced colorectal cancer(CRC). Its treatment inhibits the tumor incidence,tumor multiplicity,Ki-67 and β-catenin positive cells. The preclinical pharmacokinetics and ADME characterization of cardamonin in mice reports that cardamonin is highly permeable with an effective permeability value in ileum is(Peff)3 × 10 4 which is highly significant. Within 30 minutes of oral dosing,cardamonin is distributed to various tissues[3]. |
| Cell Experiment |
Endothelial cells are preincubated with different concentrations of cardamonin for 12 h. Then,Trypan blue-labeled BSA is added into the upper compartments of Transwell membranes. Thirty minutes later,cells are stimulated by LPS(1 μg/mL)for 1 h. Trypan blue dye content in the lower compartment is assayed by spectrophotometry at 590 nm and expressed as a percentage of the maximum concentration that would have been achieved at equilibrium.[2] |
| Animal Experiment |
Animal Models: Male ICR mice; Dosages: 0,30,and 100 mg/kg; Administration: oral[2] |
| Data Literature Source |
[1] Wang S,et al. Molecules. 2016,21(9). pii: E1145.
[2] Wei Z,et al. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2012,26(7):282-90.
[3] Shirley James,et al. Scientific Reports. 2017,7: 13945. |
| Unit |
Bottle |
| Specification |
5mg 10mM*1mL in DMSO 10mg |

 English
English
 中文
中文

 Manual Download
Manual Download

