| CAS |
1345847-93-9 |
| English Name |
Altiratinib |
| Synonyms |
;Altiratinib(DCC2701);DCC2701;altiratinib; |
| Molecular Formula |
C26H21F3N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight |
510.46 |
| Solubility |
Soluble in DMSO |
| Purity |
≥98% |
| Appearance |
Light yellow to brown Solid |
| Storage |
Powder:2-8℃,2 years;Insolvent(Mother Liquid):-20℃,6 months;-80℃,1 year |
| MDL |
MFCD28900672 |
| SMILES |
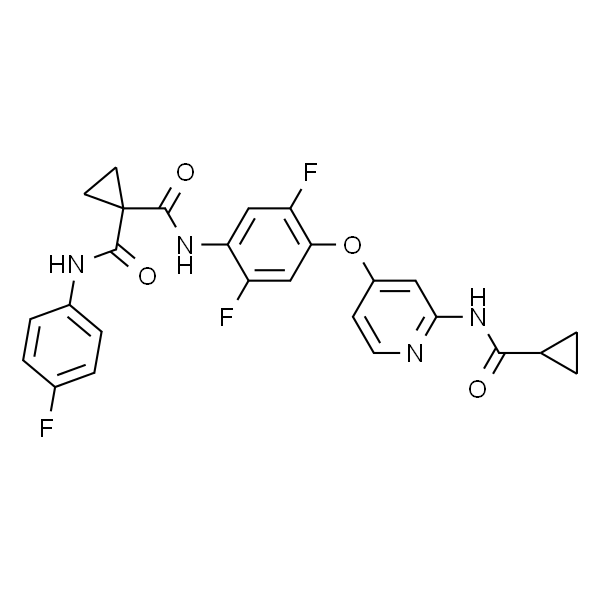
O=C(C1(C(NC2=CC=C(F)C=C2)=O)CC1)NC3=CC(F)=C(OC4=CC(NC(C5CC5)=O)=NC=C4)C=C3F |
| Target Point |
TRK;c-Met;TIE2;VEGFR2 |
| Passage |
Angiogenesis;Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK;Neuronal Signaling |
| Background |
It is a multi-target kinase inhibitor that inhibits MET, TIE2, VEGFR2, FLT3, Trk1, Trk2 and Trk3, etc. |
| Biological Activity |
Altiratinib (DCC-2701) inhibits not only mechanisms of tumor initiation and progression, but also drug resistance mechanisms in the tumor and microenvironment through balanced inhibition of MET, TIE2 (TEK), and VEGFR2 (KDR) kinases. Altiratinib durably inhibits MET, both wild-type and mutated forms, in vitro and in vivo. Through its balanced inhibitory potency versus MET, TIE2, and VEGFR2, altiratinib provides an agent that inhibits three major evasive (re)vascularization and resistance pathways (HGF, ANG, and VEGF) and blocks tumor invasion and metastasis. Altiratinib exhibits properties amenable to oral administration and exhibits substantial blood-brain barrier penetration, an attribute of significance for eventual treatment of brain cancers and brain metastases.[1] |
| In Vitro |
Altiratinib is >10-fold selective for MET versus FMS and KIT,and >50-fold selective for MET versus ABL1,FYN,HER1(EGFR),p38α(MAPK14),PDGFRα,PDGFRβ,RET,and SRC. Altiratinib exhibits IC50s of 0.69 nmol/L in K562 cells,1.2 nmol/L in SK-N-SH cells for inhibition of NGF-stimulated TRKA phosphorylation. Altiratinib inhibits constitutive TRKA phosphorylation with an IC50 of 1.4 nmol/L in KM-12 cells. Altiratinib inhibits HGF-stimulated MET phosphorylation in HUVECs,exhibiting an IC50 of 2.3 nmol/L. In ANG1-stimulated HUVECs and EA.hy926 cells,altiratinib exhibits IC50 values of 1.0 nmol/L and 2.6 nmol/L,respectively,for inhibition of TIE2 phosphorylation. In VEGF-stimulated HUVECs,altiratinib inhibits VEGFR2 phosphorylation with an IC50 of 4.7 nmol/L. Altiratinib potently inhibits cellular proliferation in MET-amplified EBC-1 and MKN-45 cells,as well as TPM3-TRKA fusion KM-12 cells,but only weakly inhibits other cancer cell lines,including proliferation of M-NFS-60(IC50,770 nmol/L); A375,BT-474,HCT-116,PC-3,SK-MEL-28,U87,and A549 cells(IC50s > 1,000 nmol/L)[1]. |
| In Vivo |
Altiratinib alone and in combination with bevacizumab increases survival and decreases circulating TIE2+-expressing monocytes in the U87 glioma model. In the PyMT syngeneic mammary tumor model which recapitulates many features of human breast cancer,altiratinib alone and in combination with paclitaxel inhibits PyMT mammary tumor growth,reduces tumoral TIE2+ stromal cell density,and inhibits lung metastasis. Altiratinib achieves a brain:plasma ratio of 0.23 after systemic dosing,indicating significant penetration of the murine blood-brain barrier[1]. |
| Cell Experiment |
Animal Models: MKN-45 xenograft mouse(Female nude mice); Dosages: 10 and 30 mg/kg; Administration: oral[1] |
| Animal Experiment |
Cells are added to 96-well(EBC-1,M-NFS-60,and SK-MEL-28: 2,500 cells/well; MKN-45: 5,000 cells/well; MV-4-11: 10,000 cells/well)or 384-well plates(A375 and HCT-116: 625 cells/well; BT-474,KM-12,PC-3,and U-87-MG: 1,250 cells/well). Plates are incubated for 72 hours. Viable cells are quantified using resazurin using a plate reader with excitation at 540 nm and emission at 600 nm.[1] |
| Data Literature Source |
1] Smith BD,et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015,14(9):2023-34. |
| Unit |
Bottle |
| Specification |
5mg 10mg |

 English
English
 中文
中文

 Manual Download
Manual Download

